One year after the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, we wanted to know: How has technology use changed over the past year in the workers’ compensation industry and how will those changes sustain through into the future? To find out, we conducted our annual survey of about 100 workers’ compensation professionals.
Download the Full Report >
Summary of 2021 Workers’ Compensation Technology Survey Results
Both telemedicine and predictive analytics were the two technologies that stood out from the 2021 workers’ compensation technology survey. The results show that the industry rapidly increased its pace of adopting or wanting to adopt these technologies during the pandemic. Here were some of our key findings.
- Technology use in the workers’ compensation industry is increasing. More than 50% of organizations reported implementing telemedicine since the start of the pandemic, and respondents overwhelmingly said that they think telemedicine (35%) and predictive analytics (35%) will have the biggest influence on the workers’ compensation industry in the next five to 10 years.
- Claims organizations are still facing challenges related to the pandemic, and are using technology to help overcome these barriers. Almost one-quarter (22%) of respondents ranked adapting to challenges from the COVID-19 pandemic as the top obstacle their organization is facing today, and 40% said they believe the pandemic is the top driver of technology adoption.
- Despite all of the technology changes in 2020, the workers’ compensation industry still has a large opportunity to introduce automation into the claims process. Only 22.5% of respondents reported that their organization uses straight-through processing for 50% or more of the medical bills they manage.
Below, we’ve detailed all of our findings from the survey and provided additional analysis.
Workers’ Compensation Tech Survey: The Results
Has your workers’ compensation organization adopted any new technologies since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic?
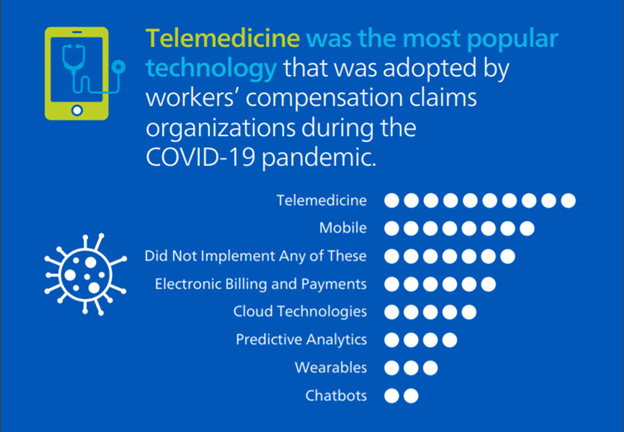
More than half of the participants said their organizations started using telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic. The next-most-adopted technology was mobile, followed by electronic payments and billing solutions, cloud technologies and predictive analytics. Only a few respondents said their companies began using wearables or chatbots, and more than a quarter of respondents said their organizations didn’t adopt any new technologies during the pandemic. We all know telemedicine usage exploded in 2020, so this finding wasn’t surprising. Moving forward, while we believe that telemedicine has a place in the workers’ compensation industry, we think there are some additional opportunities to sustain and grow usage in the coming years, including technology innovation, increased technical training for providers and permanent regulatory changes.
If you’ve implemented any of the technologies listed in question one since the start of the pandemic, which has made the biggest impact on your business?
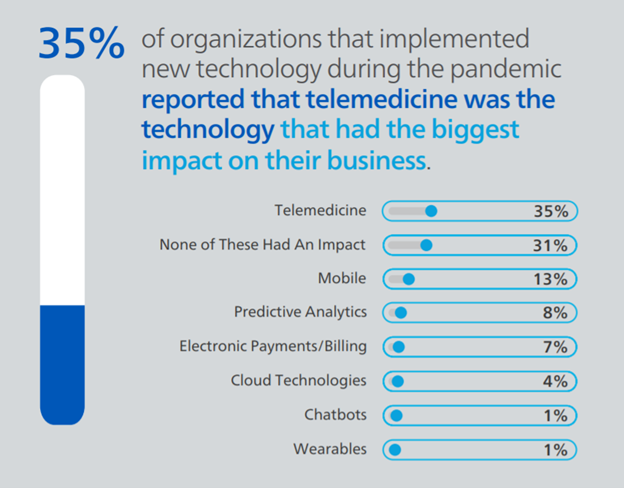
As expected, most respondents reported that telemedicine had the most substantial impact (35%) of the technologies they implemented in 2021. The second most impactful new technology was mobile (13%), followed by predictive analytics (8%) and electronic payments/billing technologies (7%). About 31% of survey participants said none of these technologies impacted their business, which aligns closely with the percentage of users who said they did not adopt any of the technologies listed in question one. It is clear from these responses and the trends we saw in the industry over the past year that telemedicine was crucial in helping continue to deliver care to injured employees during the pandemic. As we look ahead, we will watch how telemedicine plays a part in workers’ compensation claims, and which other prevalent technologies that claims organizations started using during this period have an even bigger impact in years to come.
Which advanced technology do you think will have the biggest impact on the workers’ compensation industry in the next five to 10 years?
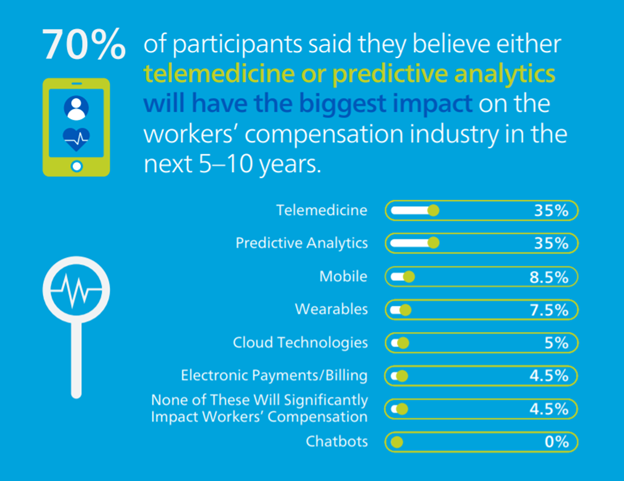
Overwhelmingly, survey respondents said that they believed both telemedicine (35%) and predictive analytics (35%) were the technologies that would have the most significant influence in the workers’ compensation industry in the next five to 10 years, compared to the other listed technologies. Mobile placed at a distant third (8.5%). These technologies have been on the industry’s mind for years. In 2020, prior to the pandemic, Mitchell conducted a similar survey and asked participants the same question—at that time, 32% of respondents said they thought telemedicine would have the biggest impact on the industry in the future and ranked artificial intelligence and predictive analytics as the next most potentially effective technologies.
Which use case do you think is, or will be, the most influential application of predictive analytics in workers’ compensation?
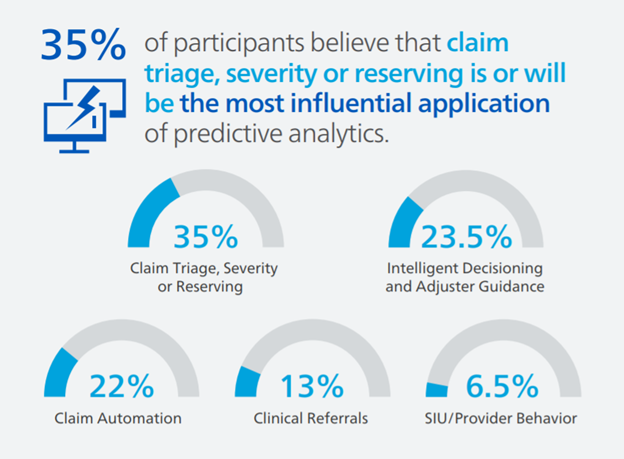
Survey respondents believe the top three most influential applications of predictive analytics in workers’ compensation are or will be claim triage, severity or reserving (35%), followed by intelligent decisioning and adjuster guidance (23.5%) and claim automation (22%). Mitchell agrees that these three applications of predictive analytics and more will be vital for efficient and effective workers’ compensation claims processing in the years to come. From triage to automation, predictive analytics can help claims organizations get the right information at the right time to make intelligent and informed claim decisions.
Which use case do you think is, or will be, the most influential application of telemedicine in workers’ compensation?

The majority of survey respondents said the best application of telemedicine is or will be for provider visits (54%). A few others said they thought nurse case management (25.5%) or triage (20.5%) are, or will be, the most influential use cases. Provider visits have been the primary use of this technology in the industry so far, so this response doesn’t surprise us. We think that with some innovation and the addition of other technologies (such as wearables, for example), telemedicine has the potential for broader use cases in the industry and could serve a more vital purpose in helping improve claim outcomes for injured employees.
Which of these factors do you think is the most influential reason the workers' compensation industry is adopting advanced technologies?
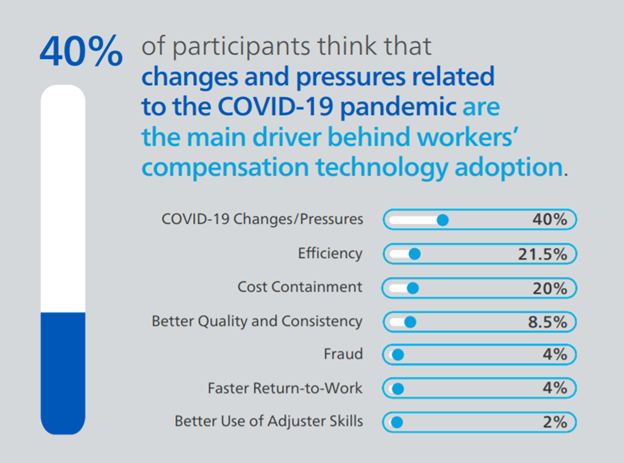
Changes and pressures from the COVID-19 pandemic was the top reason participants said they believe the industry is adding new, advanced technologies (40%). While this was reported as the top driver for change, claims organizations are still looking to solve challenges that existed before the pandemic (and may have been exasperated by everything that happened in the past year). Efficiency (21.5%) was rated as the second top driver of technology adoption, followed closely by cost containment (20%). As COVID-19 vaccines continue to roll out across the country and the world, it will be interesting to see how long it takes the industry to overcome the challenges the pandemic brought forth and if technology plays an even bigger role moving forward as we all prepare not only for a post-pandemic world, but also for whatever challenges lie ahead.
What percent of individual medical bills does your company process using straight-through process automation?
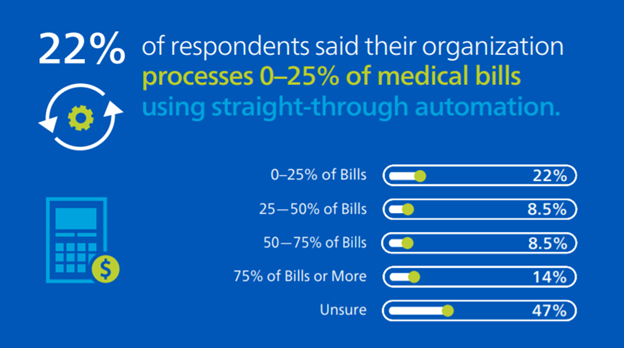
Despite the rapid rate of technology adoption in the past year, the workers’ compensation industry still has a significant opportunity for automation. Less than a quarter of respondents (22.5%) said they automate 50% or more of workers’ compensation medical bills using straight-through processing and 22% of respondents said they process 25% or fewer of their bills automatically. Typically, an efficient workflow passes 60-70% of medical bills through without human intervention, and it is clear the industry still has a lot of opportunity to reach this level of automation. Straight-through-processing offers many benefits, including removing repeatable tasks from your adjusters’ workload, boosting consistency and freeing your employees up to have more time to focus on complex claims that need extra scrutiny and care to help achieve better outcomes.
What percent of claims does your company process using straight-through process automation?
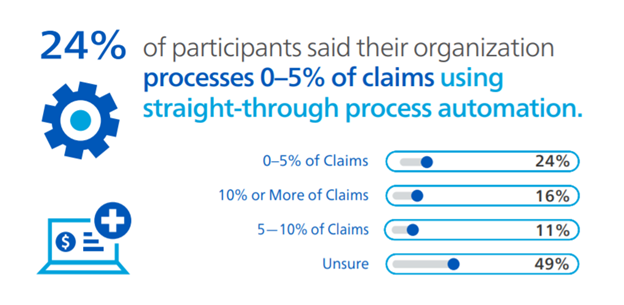
Even fewer respondents said their organization processes workers’ compensation claims automatically. Only 16% said they use straight-through process automation for 10% or more of their claims, and about a quarter (24%) said they only automatically process 0-5% of claims. We all know that we may never achieve full automation of all workers’ compensation claims—unlike other lines of insurance, some workers’ compensation claims will always require a level of human touch. Though we may not be looking to process every single workers’ compensation claim straight through, there are still plenty of opportunities to boost automation today and in the future using rules engines, artificial intelligence like predictive analytics and more. As technologies become more advanced in the years to come, claims organizations will need to think about how they can strike the right balance and implement the appropriate level of automation that allows them to spend their time focusing on the claims that need special attention.
Out of the options below, what is the biggest claims challenge your organization is facing today?
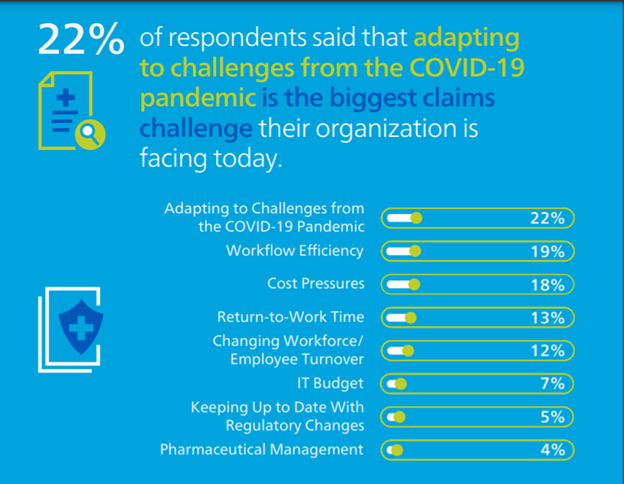
While participants said adapting to challenges from the COVID-19 pandemic is the most prominent obstacle their organization is facing today (22%), even more respondents said they thought cost pressures and workflow efficiency combined are currently their biggest hurdles (37% combined). While the pandemic is still making waves across the industry and probably will for at least months to come, if not more, it is interesting to see many organizations are still facing some of the same challenges they were up against pre-pandemic. In the 2020 survey, respondents said workflow efficiency was the most significant challenge they faced (27%) followed by cost containment (19%).
Survey Demographics
Mitchell surveyed nearly 100 workers’ compensation professionals at a range of companies, including insurance carriers, third-party administrators, public entities, managed care and risk management organizations, and brokers. The majority of respondents (75%) had 10 or more years of experience in the workers’ compensation industry.
Register for our Webinar
For additional analysis of the survey results, including a deep dive into predictive analytics, automation and telemedicine, register now for our upcoming webinar on May 13 at 9 am PT.


